
Our services
Routine care

Routine check-ups with X-rays should be scheduled every six months. Regular visits help us catch early signs of dental issues before they become painful. X-rays detect cavities that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Digital radiographs
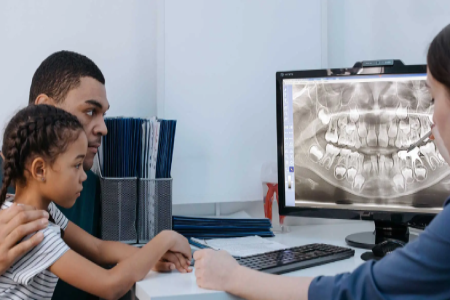
Digital radiographs provide clear, magnified images, offering a more accurate view. They allow us to enlarge the image for a more precise diagnosis and have lower radiation exposure than traditional X-rays. We follow all safety protocols to ensure your child’s well-being.
Cleaning
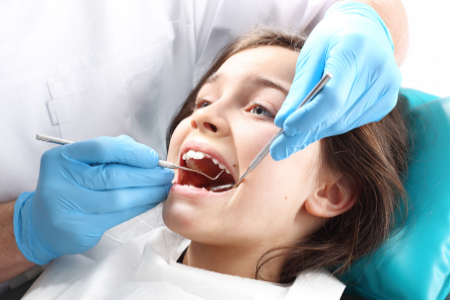
Prophylaxis is done at check-ups to remove plaque and tartar from your child’s teeth, which brushing alone can’t do. It helps prevent gum disease and cavities. When cleaning a special electric brush to polish the teeth is used.
Fluoride
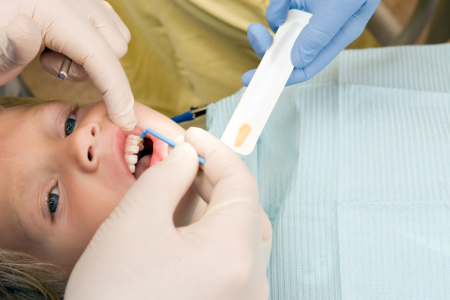
Fluoride may be applied after dental cleaning to protect your child’s teeth from cavities for several months. Using a small brush, fluoride varnish is applied directly to the teeth to remineralize tooth enamel and prevent decay.
Sealants
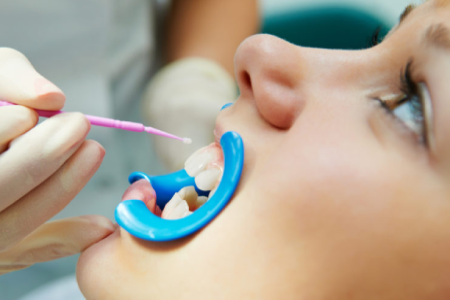
Sealants are thin, white plastic coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of molars to prevent cavities. These areas are prone to plaque buildup and decay, especially in children and teens. Sealants, along with fluoride, help protect teeth. With proper care, they can last 5 to 10 years. Avoid giving your child crunchy foods, ice, or hard candies to extend their longevity.
Composite resin
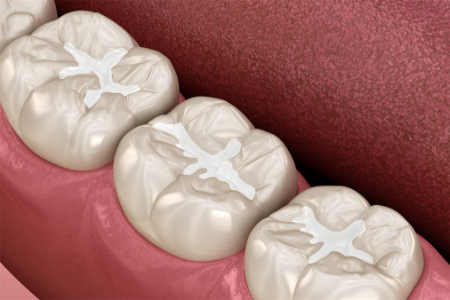
Tooth-colored fillings are used to restore decayed or broken front and back teeth. Made from composite materials, these fillings match the natural color of your child's teeth for a more aesthetic, seamless look.
Stainless steel crowns
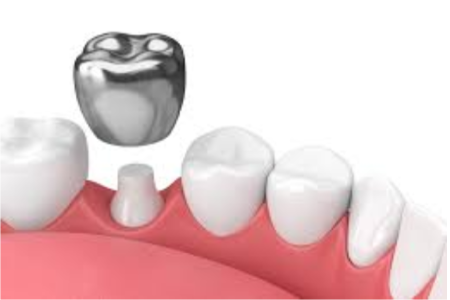
When molars are too damaged to be repaired with fillings, silver-colored crowns are used to restore the tooth. These crowns help protect the tooth from further decay or damage until natural tooth loss occurs.
Baby root canal

A pulpotomy treats infected blood vessels and nerves in a tooth, typically needed due to severe tooth decay or injury. If left untreated, the child may experience pain, infection, swelling, or even tooth loss. Our goal is to save the tooth until the permanent one comes in, avoiding extraction and the need for space maintenance.
Extractions
Extractions are only performed in severe cases of tooth decay. If a primary molar is extracted early, a space maintainer is placed to preserve the space for the permanent tooth. Extractions are our last resource because primary teeth are the best space maintainers.
Space maintainers
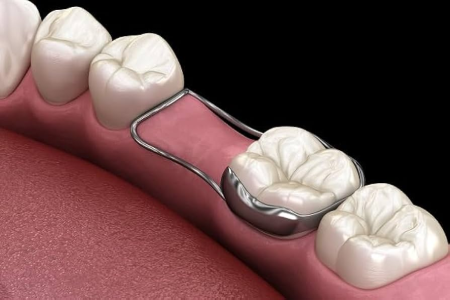
When a primary tooth is lost early, space maintainers are used to keep the space for the permanent tooth. Without a space maintainer, neighboring teeth may shift, which can delay the permanent tooth's eruption. The space maintainer is removed once the permanent tooth is ready to erupt.
Brackets and aligners

Children should have their first orthodontic consultation around the age of 6 or 7 when the first permanent molars and front teeth erupt. This consultation helps monitor tooth development, identify any bite issues or crooked teeth, and determine the need for interceptive orthodontics to guide the teeth, thus preventing the need for more complex treatments later.

